Excel worksheets combination
new header
new 2nd header
new level
What if our Client provides us with a number of poorly recorded databases with thousands of records in different Excel formats? not only that, within each Excel file, there are hundreds of worksheets with in-homogeneous structures –F.. Excel ^_^, but that is the reality, particularly when we have to work with Clients whose business are not much involved with TECH.
What if our Client provides us with a number of poorly recorded databases with thousands of records in different Excel formats? not only that, within each Excel file, there are hundreds of worksheets with in-homogeneous structures –F…. Excel ^_^, but that is the reality, particularly when we have to work with Clients whose business are not much involved with TECH.
Let start with time series data that is saved in hundreds of excel worksheets, examples are
- Production and consumption data of a single day. Within a day, volumes of production and consumption (e.g. water and energy of a water treatment plant or pump station, number of X and Y produced within a single hours);
- Hydrology data such as rainfall and runoff and other associated parameters etc
Ideally, those data should be recorded using relational database structured system such as MySQL or PostgreSQL. However, by default in many organizations, data is recorded in excel file. Everyday, owner of the file just multiply/copy the same worksheet of previous day and repeat the same work. This is OK for him/her but definitely not OK for us, the analyst :).
This post describes a step by step instruction on how to deal with this issue.
Examples
Data
Example data is with two excel files name data1 and data2. These two files have their structure identical as shown in the followings
data1
worksheet1
date from to total_pro_hour total_power_hour ratio
01-Jan-17 12:00 AM1:00 AM 0.7700000 95 123.38
01-Jan-17 1:00 AM 2:00 AM 0.7400000 86 116.22
01-Jan-17 2:00 AM 3:00 AM 0.6200000 73 117.74
01-Jan-17 3:00 AM 4:00 AM 0.6100000 70 114.75
01-Jan-17 4:00 AM 5:00 AM 0.5700000 62 108.77
01-Jan-17 5:00 AM 6:00 AM 0.7300000 86 117.81
01-Jan-17 6:00 AM 7:00 AM 0.6900000 70 101.45
01-Jan-17 7:00 AM 8:00 AM 1.0100000 93 92.08
01-Jan-17 8:00 AM 9:00 AM 0.9100000 116 127.47
01-Jan-17 9:00 AM 10:00AM 1.0800000 120 111.11
01-Jan-17 10:00 AM 11:00AM 1.0900000 122 111.93
01-Jan-17 11:00 AM 12:00PM 1.0800000 119 110.19
01-Jan-17 12:00 PM 1:00PM 1.1000000 117 106.36
01-Jan-17 1:00 PM 2:00 PM 1.5420000 145 94.03
01-Jan-17 2:00 PM 3:00 PM 0.9330000 136 145.77
01-Jan-17 3:00 PM 4:00 PM 1.0520000 137 130.23
01-Jan-17 4:00 PM 5:00 PM 0.9600000 153 159.38
01-Jan-17 5:00 PM 6:00 PM 0.9910000 135 136.23
01-Jan-17 6:00 PM 7:00 PM 1.0110000 146 144.41
01-Jan-17 7:00 PM 8:00 PM 0.9320000 134 143.78
01-Jan-17 8:00 PM 9:00 PM 0.9680000 133 137.40
01-Jan-17 9:00 PM 10:00 PM 0.7110000 124 174.40
01-Jan-17 10:00 PM 11:00 PM 0.7800000 72 92.31
01-Jan-17 11:00 PM 12:00 AM 0.6100000 75 122.95
worksheet 2
02-Jan-17 12:00 AM 1:00 AM 0.5600000 48 85.71
02-Jan-17 1:00 AM 2:00 AM 0.4420000 42 95.02
02-Jan-17 2:00 AM 3:00 AM 0.4700000 40 85.11
02-Jan-17 3:00 AM 4:00 AM 0.6980000 59 84.53
02-Jan-17 4:00 AM 5:00 AM 0.8200000 86 104.88
02-Jan-17 5:00 AM 6:00 AM 0.4700000 48 102.13
02-Jan-17 6:00 AM 7:00 AM 1.0400000 121 116.35
02-Jan-17 7:00 AM 8:00 AM 1.0800000 146 135.19
02-Jan-17 8:00 AM 9:00 AM 1.0800000 122 112.96
02-Jan-17 9:00 AM 10:00 AM 0.9600000 82 85.42
02-Jan-17 10:00 AM 11:00 AM 0.9100000 73 80.22
02-Jan-17 11:00 AM 12:00 PM 0.8500000 65 76.47
02-Jan-17 12:00 PM 1:00 PM 0.7100000 57 80.28
02-Jan-17 1:00 PM 2:00 PM 0.9690000 48 49.54
02-Jan-17 2:00 PM 3:00 PM 0.8310000 65 78.22
02-Jan-17 3:00 PM 4:00 PM 1.1290000 96 85.03
02-Jan-17 4:00 PM 5:00 PM 1.2300000 109 88.62
02-Jan-17 5:00 PM 6:00 PM 1.1210000 114 101.69
02-Jan-17 6:00 PM 7:00 PM 0.9440000 110 116.53
02-Jan-17 7:00 PM 8:00 PM 0.9790000 112 114.40
02-Jan-17 8:00 PM 9:00 PM 1.0260000 108 105.26
02-Jan-17 9:00 PM 10:00 PM 0.8710000 118 135.48
02-Jan-17 10:00 PM 11:00 PM 0.8100000 99 122.22
02-Jan-17 11:00 PM 12:00 AM 0.6800000 79 116.18
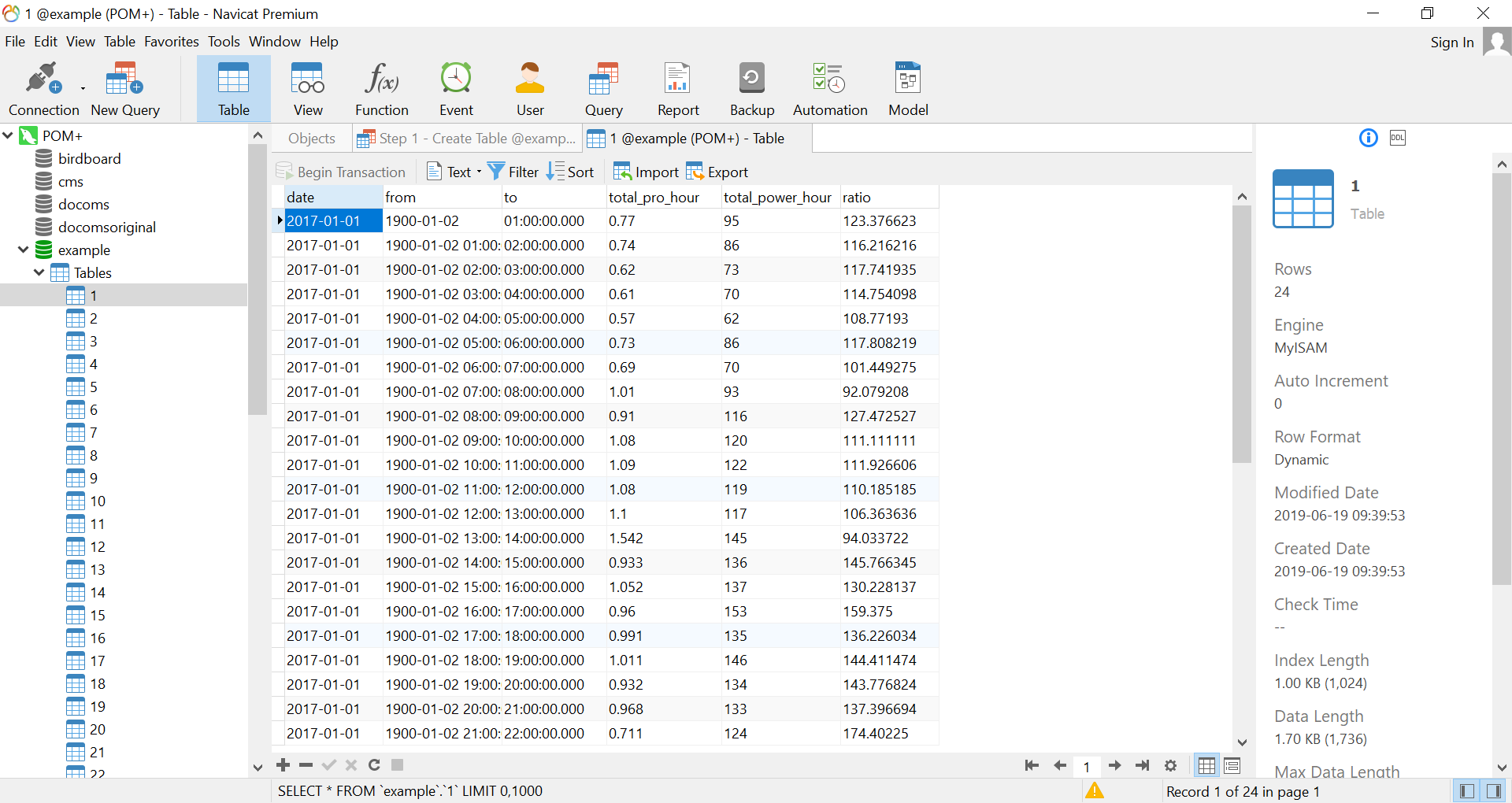
This excel file contains 2 worksheet “1” and “2” that record hourly production (ML) and energy consumption (KW) of a water pump station.
- column is the date;
- column 2 and 3 are hours;
- column 4 is production data in million liter (ML);
- column 5 is energy consumption data in KW
- column 6 is ratio between energy consumption and production, basically it is the division of column 5 and 4.
This kind of data is recorded hourly and there will be about 30 worksheets for one month. Let say you have 5 or 10 years production data saving in excel files like this and you need to combine all of them into a single frame for Business Analysis purpose. It will be a nightmare if you just copy and paste 🙂 terrible excel.
Assumptions
It is assumed that all worksheets in all excel files are identical in their structure. This is not a realistic assumption as excel users cannot be consistent with their data. Data in their excel files are
Mixed up with numeric and text even for the same attributes; Merging cells, adding new rows and columns that make them homogeneous. Solving such problem is not the objective of this post, but it is worth to mention that before we get a good set of data, we probably need to do some Coding in Visual Basic to standardize the excel worksheets, or we need to do a certain level of manual data compiling before we can run the code in R.
Will cover how to standardize using the same sets of data in other post.
Combining worksheets using Navicat and MySQL
Why NAVICAT?
–> Navicat offers a handy way to import data from excel files. It can import multiple worksheets in one single click into respective tables of MySQL. I find this feature superior than other open source SQL Client such PhPmyAdmin, Dbeaver, etc.
Herein, I demonstrate some steps to import the example data files.
a. Create table
create
table
`1` (
date varchar(255),
`from` varchar(255),
`to` varchar(255),
total_pro_hour varchar(255),
total_power_hour varchar(255),
ratio varchar(255)
);
create table `2` as select * from `1`;
create table `3` as select * from `1`;
create table `4` as select * from `1`;
create table `5` as select * from `1`;
create table `6` as select * from `1`;
create table `7` as select * from `1`;
create table `8` as select * from `1`;
create table `9` as select * from `1`;
create table `10` as select * from `1`;
create table `11` as select * from `1`;
create table `12` as select * from `1`;
create table `13` as select * from `1`;
create table `14` as select * from `1`;
create table `15` as select * from `1`;
create table `16` as select * from `1`;
create table `17` as select * from `1`;
create table `18` as select * from `1`;
create table `19` as select * from `1`;
create table `20` as select * from `1`;
create table `21` as select * from `1`;
create table `22` as select * from `1`;
create table `23` as select * from `1`;
create table `24` as select * from `1`;
create table `25` as select * from `1`;
create table `26` as select * from `1`;
create table `27` as select * from `1`;
create table `28` as select * from `1`;
create table `29` as select * from `1`;
create table `30` as select * from `1`;
This SQL creates 30 tables name from 1 to 30 that correspond to each day in a month. Note that for February, there are 28 days but dont worry, we still use 30 or 31 worksheets as additional worksheets will be blank anyway and make no harm to the operation.
b. Manual importing worksheets from the excel file to MySQL table using NaviCAT
- Select table 1 in MySQL database
- Right Click –> Import Wizard
- Select Excel file and Click Next
- Import the excel file
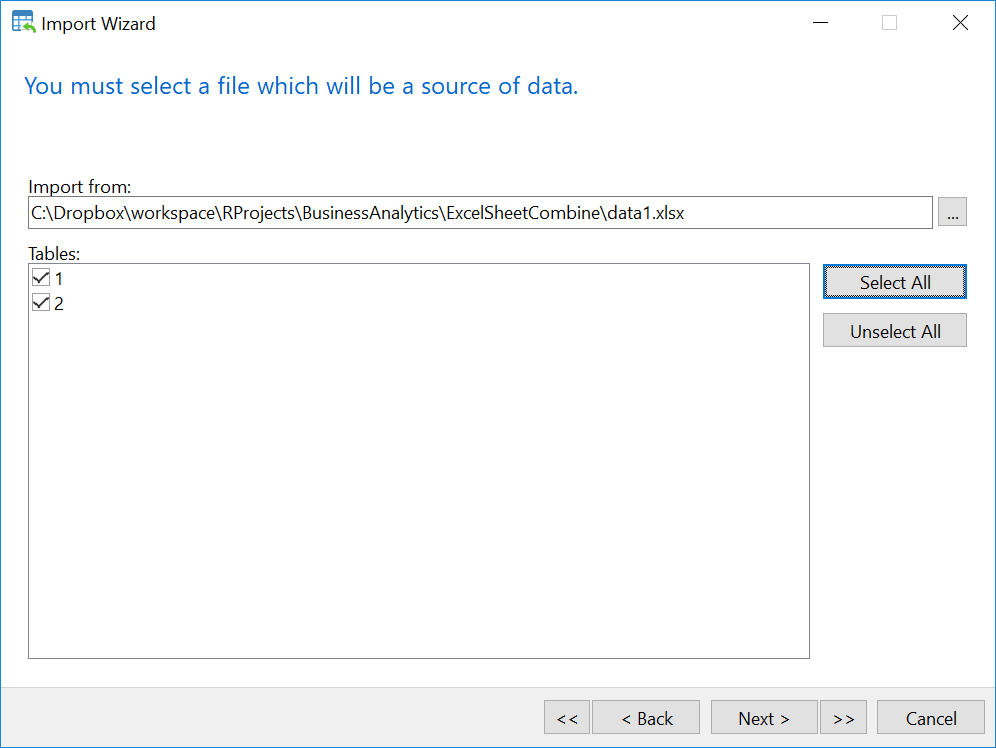
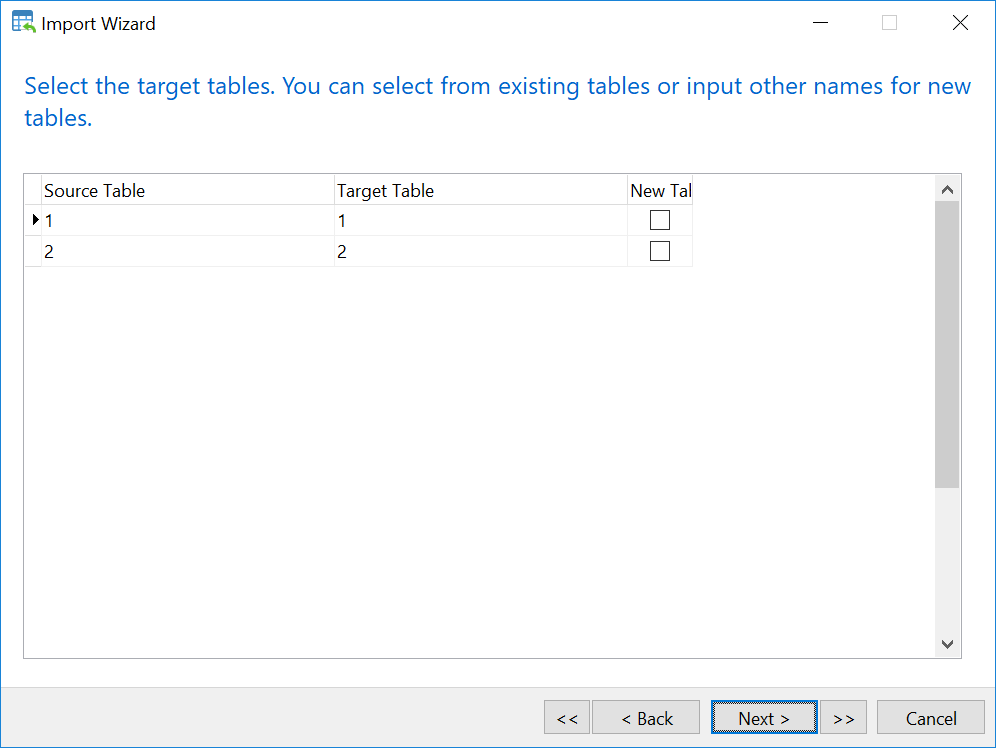
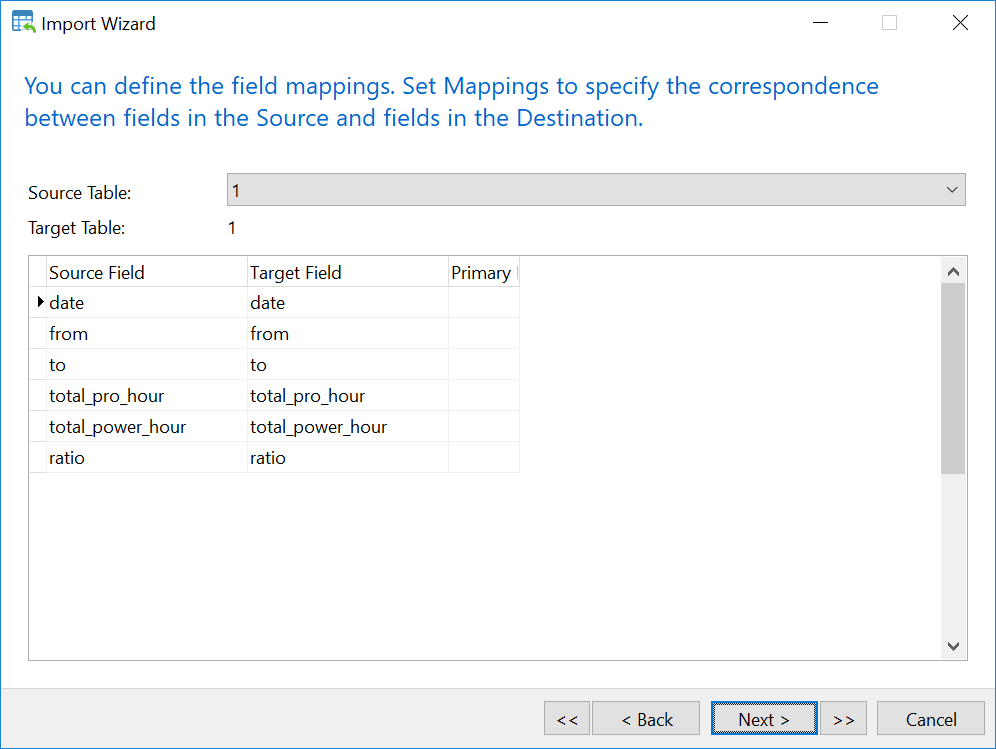
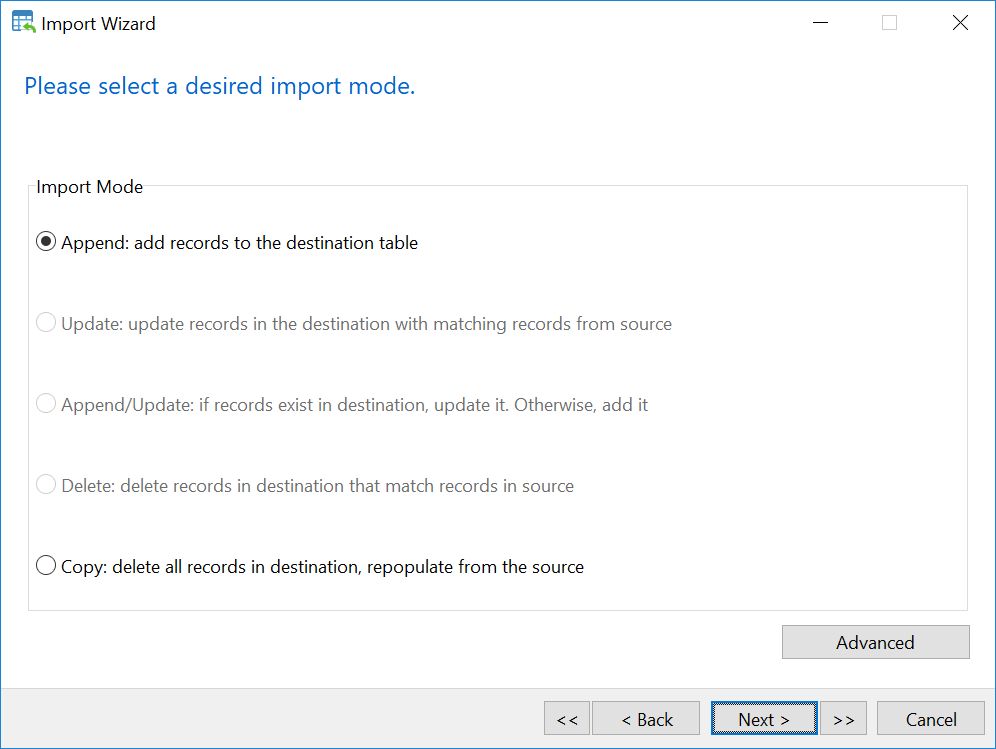
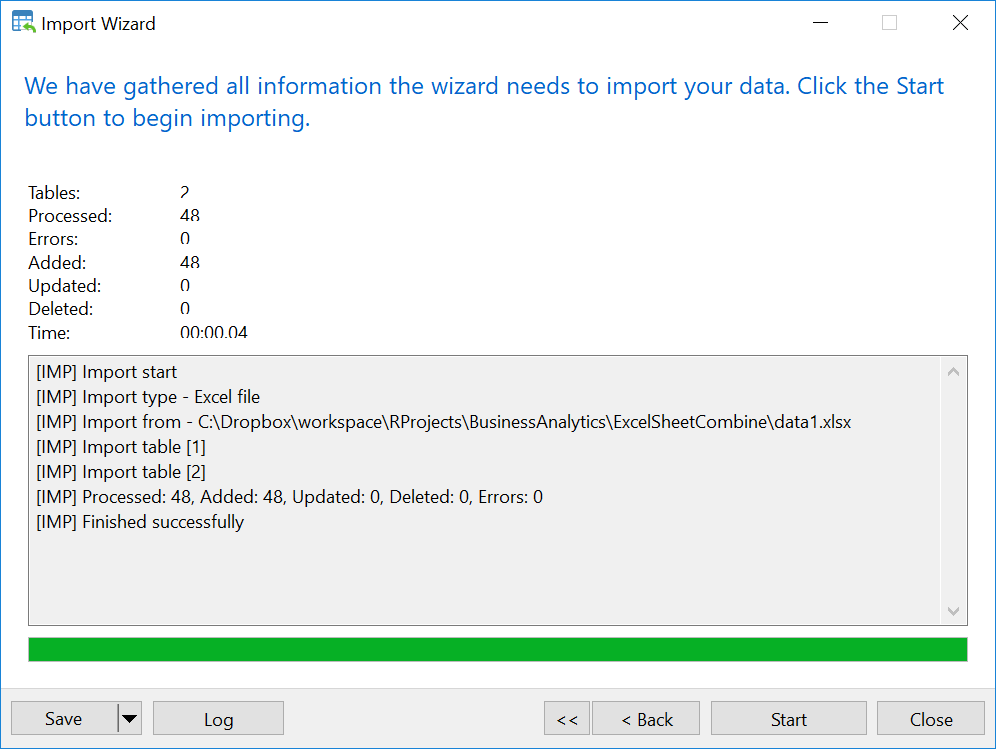
Now you have all tables you need in MySQL. However, Values of time shown in FROM and TO column have change from AM, PM to something else. For example 1900-01-02 should be 24. To solve this issue, we will use the following SQL syntax
c. Rename tables
RENAME TABLE
`1` TO pat_2018_10_1,
`2` TO pat_2018_10_2,
`3` TO pat_2018_10_3,
`4` TO pat_2018_10_4,
`5` TO pat_2018_10_5,
`6` TO pat_2018_10_6,
`7` TO pat_2018_10_7,
`8` TO pat_2018_10_8,
`9` TO pat_2018_10_9,
`10` TO pat_2018_10_10,
`11` TO pat_2018_10_11,
`12` TO pat_2018_10_12,
`13` TO pat_2018_10_13,
`14` TO pat_2018_10_14,
`15` TO pat_2018_10_15,
`16` TO pat_2018_10_16,
`17` TO pat_2018_10_17,
`18` TO pat_2018_10_18,
`19` TO pat_2018_10_19,
`20` TO pat_2018_10_20,
`21` TO pat_2018_10_21,
`22` TO pat_2018_10_22,
`23` TO pat_2018_10_23,
`24` TO pat_2018_10_24,
`25` TO pat_2018_10_25,
`26` TO pat_2018_10_26,
`27` TO pat_2018_10_27,
`28` TO pat_2018_10_28,
`29` TO pat_2018_10_29,
`30` TO pat_2018_10_30
;
Here we rename the table to whatever we need. By doing so, we can resue the Create Query to perform the same procedure for importing new table.
d. Create Production table
create
table
production (
date varchar(255),
`from` varchar(255),
`to` varchar(255),
total_pro_hour varchar(255),
total_power_hour varchar(255),
ratio varchar(255)
);
This code creates a production table.
e. Import/Append all raw tables into one table – Production
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_1;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_2;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_3;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_4;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_5;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_6;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_7;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_8;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_9;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_10;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_11;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_12;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_13;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_14;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_15;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_16;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_17;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_18;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_19;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_20;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_21;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_22;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_23;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_24;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_25;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_26;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_27;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_28;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_29;
INSERT INTO production
SELECT *
FROM pat_2017_1_30;
This code imports all data from raw table into production table.
f. Correct data, particularly with date and time
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS productioncorrected;
create table productioncorrected select * from production;
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'1900-01-01','24:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'1900-01-02 ','');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'1900-01-02','00:00:00.000');
#####
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'1:00AM','01:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'2:00AM','02:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'3:00AM','03:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'4:00AM','04:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'5:00AM','05:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'6:00AM','06:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'7:00AM','07:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'8:00AM','08:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'9:00AM','09:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'10:00AM','10:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'11:00AM','11:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'12:00PM','12:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'01:00PM','13:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'02:00PM','14:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'03:00PM','15:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'04:00PM','16:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'05:00PM','17:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'06:00PM','18:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'07:00PM','19:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'08:00PM','20:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'09:00PM','21:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'10:00PM','22:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'11:00PM','23:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,'12:00AM','00:00:00.000');
#####
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'1:00AM','01:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'2:00AM','02:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'3:00AM','03:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'4:00AM','04:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'5:00AM','05:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'6:00AM','06:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'7:00AM','07:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'8:00AM','08:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'9:00AM','09:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'10:00AM','10:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'11:00AM','11:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'12:00PM','12:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'01:00PM','13:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'02:00PM','14:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'03:00PM','15:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'04:00PM','16:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'05:00PM','17:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'06:00PM','18:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'07:00PM','19:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'08:00PM','20:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'09:00PM','21:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'10:00PM','22:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'11:00PM','23:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,'12:00AM','24:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,' 101:00:00.000','11:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = replace(productioncorrected.`to`,' 102:00:00.000','24:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,' 101:00:00.000','11:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = replace(productioncorrected.`from`,' 102:00:00.000','24:00:00.000');
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = "24:00:00.000"
WHERE productioncorrected.`from`= "23:00:00.000";
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`to` = "11:00:00.000"
WHERE productioncorrected.`from`= "10:00:00.000";
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = "11:00:00.000"
WHERE productioncorrected.`to`= "12:00:00.000";
UPDATE productioncorrected SET productioncorrected.`from` = "24:00:00.000"
WHERE productioncorrected.`to`= "01:00:00.000";
This code is used to correct
- time data
- missing data
- outliner
g. Create analysis table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS analysis;
CREATE TABLE analysis
Select *
from
productioncorrected
where productioncorrected.total_pro_hour >0
and
productioncorrected.total_power_hour>0
and
productioncorrected.total_power_hour NOT LIKE "-"
;
ALTER TABLE analysis MODIFY COLUMN total_power_hour DOUBLE;
ALTER TABLE analysis MODIFY COLUMN total_pro_hour DOUBLE;
ALTER TABLE analysis MODIFY COLUMN ratio DOUBLE;
Analysis table is basically the same with production but with some correction
h. Create Analysis Date table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS analysisdate;
CREATE TABLE analysisdate
Select
*
from
analysis
GROUP BY analysis.date;
ALTER TABLE analysisdate
ADD id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY;
This SQL code will create Analysis Date table that basically summary hourly data into daily data.
WHAO, after going through each of the above Query, my figures are tired already. You can further enhance SQL code to make the entire process faster, but still it is much slower than using below R code.
Combining worksheets using R
Below R codes are extracted from Github source
This code is used to combine multiple excel worksheets into one dataframe. Particularly useful when combining multiple worksheets of production data with each worksheet is a date of a month, and in each worksheet, data is saved in hourly basis.
the first method, using XlConnect.
# this method has a limitation that XlConnect doesnt work well with excel files with dynamic links. When importing into R, it gives NA values.
# to make sure that importing is perfect. It is advisable to disable all dynamic links in excel file by going to Data
library(XLConnect)
# load data file (excel files ended with cls, xlsc, or xlsm)
datafile <- loadWorkbook("data1.xlsx") # This is a static worksheet, without any dynamic links
# obtain sheet names
worksheets <- getSheets(datafile)
names(worksheets) <- worksheets
# dataframe
worksheets_list <- lapply(worksheets, function(.sheet){readWorksheet(object=datafile, .sheet)})
# limit worksheet_list to sheets with at least 1 dimension
worksheets_list2 <- worksheets_list[sapply(worksheets_list, function(x) dim(x)[1]) > 0]
# code to read in each excel worksheet as individual dataframes
for (i in 2:length(worksheets_list2)){assign(paste0("df", i), as.data.frame(worksheets_list2[i]))}
# define function to clean data in each data frame (updated based on your data). You must define here carefully otherwise it will not work well with some certain type of data. The fastest way is only drop out missing values. Other value can be dealed with using query in MySQL
cleaner <- function(df){
# drop rows with missing values
df <- df[rowSums(is.na(df)) == 0,]
# remove serial comma from all variables
# df[,-1] <- as.numeric(gsub(",", "", as.matrix(df[,-1])))
# create numeric version of year variable for graphing
# df$Year <- as.numeric(substr(df$year, 1, 4))
# return cleaned df
return(df)
}
# clean sheets and create one data frame
data1 <- do.call(rbind,lapply(names(worksheets_list2), function(x) cleaner(worksheets_list2[[x]])))
cat("Print out the data 1 frame \n")
print(data1)
# Method is with readxl package. This is superior than the former one as readxl can handle excel files with dynamic links. This means it will retain values and ignore the links.
# ----------------
library(readxl)
read_excel_allsheets <- function(filename, tibble = FALSE) {
# I prefer straight data.frames
# but if you like tidyverse tibbles (the default with read_excel)
# then just pass tibble = TRUE
sheets <- readxl::excel_sheets(filename)
x <- lapply(sheets, function(X) readxl::read_excel(filename, sheet = X))
if(!tibble) x <- lapply(x, as.data.frame)
names(x) <- sheets
x
}
#start to read and write data into csv file
worksheets <- read_excel_allsheets("data1.xlsx")
source("cleaning.R")
filedata <- do.call(rbind,lapply(names(worksheets), function(x) cleaner(worksheets[[x]])))
write.table(filedata, "myDF.csv", sep = ",", col.names = !file.exists("myDF.csv"), row.names=FALSE, append = T)
worksheets <- read_excel_allsheets("data2.xlsm")
source("cleaning.R")
filedata <- do.call(rbind,lapply(names(worksheets), function(x) cleaner(worksheets[[x]])))
write.table(filedata, "myDF.csv", sep = ",", col.names = !file.exists("myDF.csv"), row.names=FALSE, append = T)
#end
#https://medium.com/@niharika.goel/merge-multiple-csv-excel-files-in-a-folder-using-r-e385d962a90a
Combining multiple excel files using R
I found the code from Niharika suits the purpose of this exercise. Kindly refer to her github site for original code.
https://github.com/NiharikaGoel12/R-Playground
Her readme file states This repository contains basic codes for R, which might be useful in day to day work, especially doing data analysis on large datasets in Excel or CSV.
#Merge multiple Excel/CSV files in a folder
Consider a case when you have multiple xlsx/csv files in a folder & you to merge them into one single file. Here, I have used lapply() which returns a list of the same length as i. And grepl() will check exact match between merge_file_name & existing file ‘i’. In this case, if the two files are same, we will ignore already created “merge file”.
rbind() will combine data frame by rows and merge all the files.
a. Combining CSV files
path <- "sample-data/merge-files/csv"
merge_file_name <- "sample-data/merge-files/merged_file.csv"
filenames <- list.files(path= path, full.names=TRUE)
All <- lapply(filenames,function(filename){
print(paste("Merging",filename,sep = " "))
read.csv(filename)
})
df <- do.call(rbind.data.frame, All)
write.csv(df,merge_file_name)
b. Combining excel files
library(openxlsx)
path <- "sample-data/merge-files/xlsx"
merge_file_name <- "sample-data/merge-files/merged_file.xlsx"
filenames_list <- list.files(path= path, full.names=TRUE)
All <- lapply(filenames_list,function(filename){
print(paste("Merging",filename,sep = " "))
read.xlsx(filename)
})
df <- do.call(rbind.data.frame, All)
write.xlsx(df,merge_file_name)
c. Combining the example data
We can use the code in step a and b of this section. However, there is one draw back that we need to save our data first into csv or excel file. This is also a bit of time consuming. To avoid this, we can just simply write directly data into csv file as presented in the last part of section 4.
# ----------------
library(readxl)
read_excel_allsheets <- function(filename, tibble = FALSE) {
# I prefer straight data.frames
# but if you like tidyverse tibbles (the default with read_excel)
# then just pass tibble = TRUE
sheets <- readxl::excel_sheets(filename)
x <- lapply(sheets, function(X) readxl::read_excel(filename, sheet = X))
if(!tibble) x <- lapply(x, as.data.frame)
names(x) <- sheets
x
}
#start to read and write data into csv file
worksheets <- read_excel_allsheets("data1.xlsx")
source("cleaning.R")
filedata <- do.call(rbind,lapply(names(worksheets), function(x) cleaner(worksheets[[x]])))
write.table(filedata, "myDF.csv", sep = ",", col.names = !file.exists("myDF.csv"), row.names=FALSE, append = T)
worksheets <- read_excel_allsheets("data2.xlsm")
source("cleaning.R")
filedata <- do.call(rbind,lapply(names(worksheets), function(x) cleaner(worksheets[[x]])))
write.table(filedata, "myDF.csv", sep = ",", col.names = !file.exists("myDF.csv"), row.names=FALSE, append = T)
#end
The above code read 2 data files data1.xlsx and data2.xlsm, combining all worksheets of these two files and then write the data frame to a CSV file named myDF.csv. If we have more than 2 files to read and combine, we can just copy the code and paste it under and remember to change the source data file. We can also automate this process by making a loop, which will be presented in other post.
Once we have the combined CSV file, we can use NaviCAT to import this file to MySQL for further enhancement as presented in section 3. In the end, we can summary the production and energy consumption data in day or week that will be useful for visualization, correlation, and regression analysis.
Visualization
Tableu
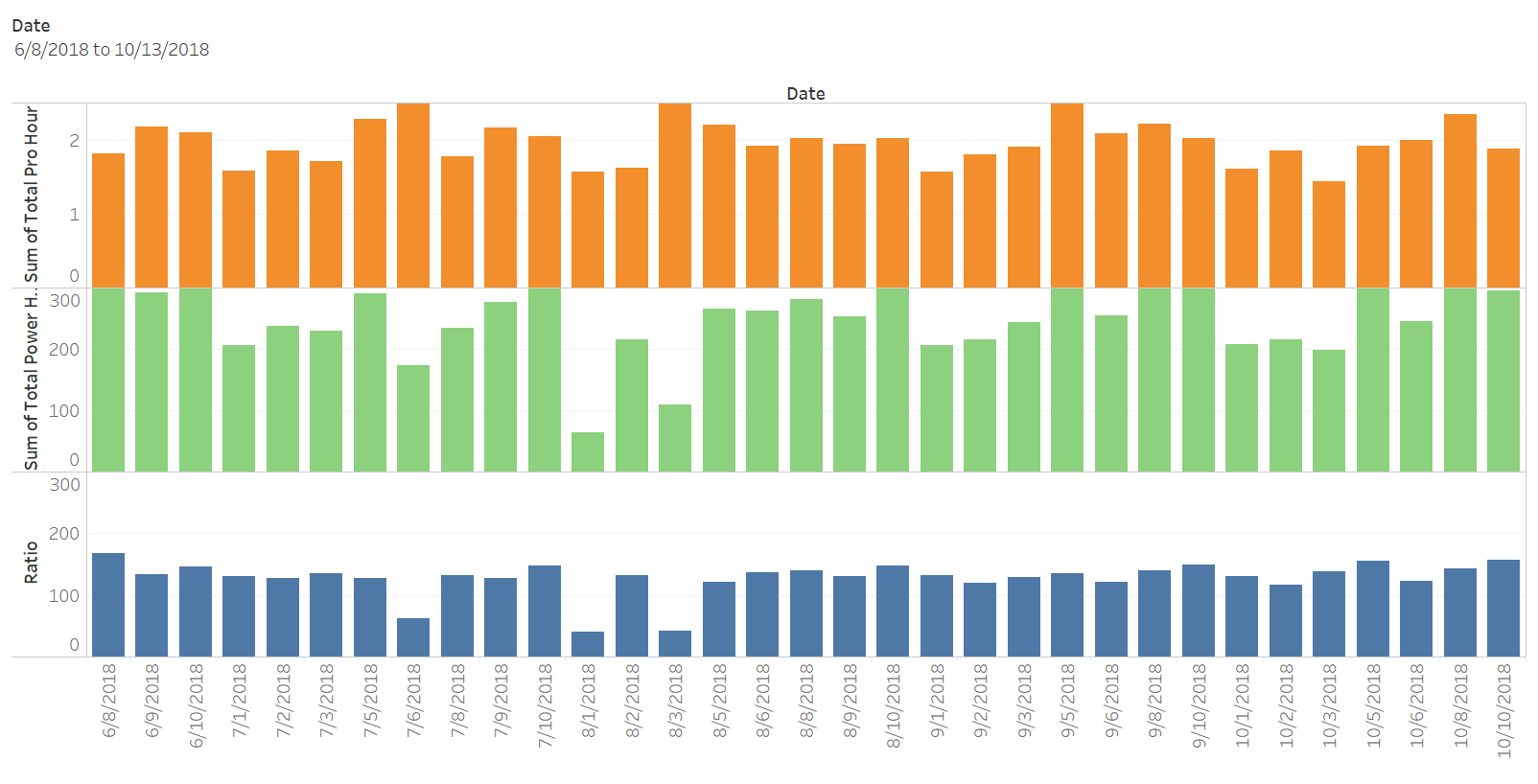
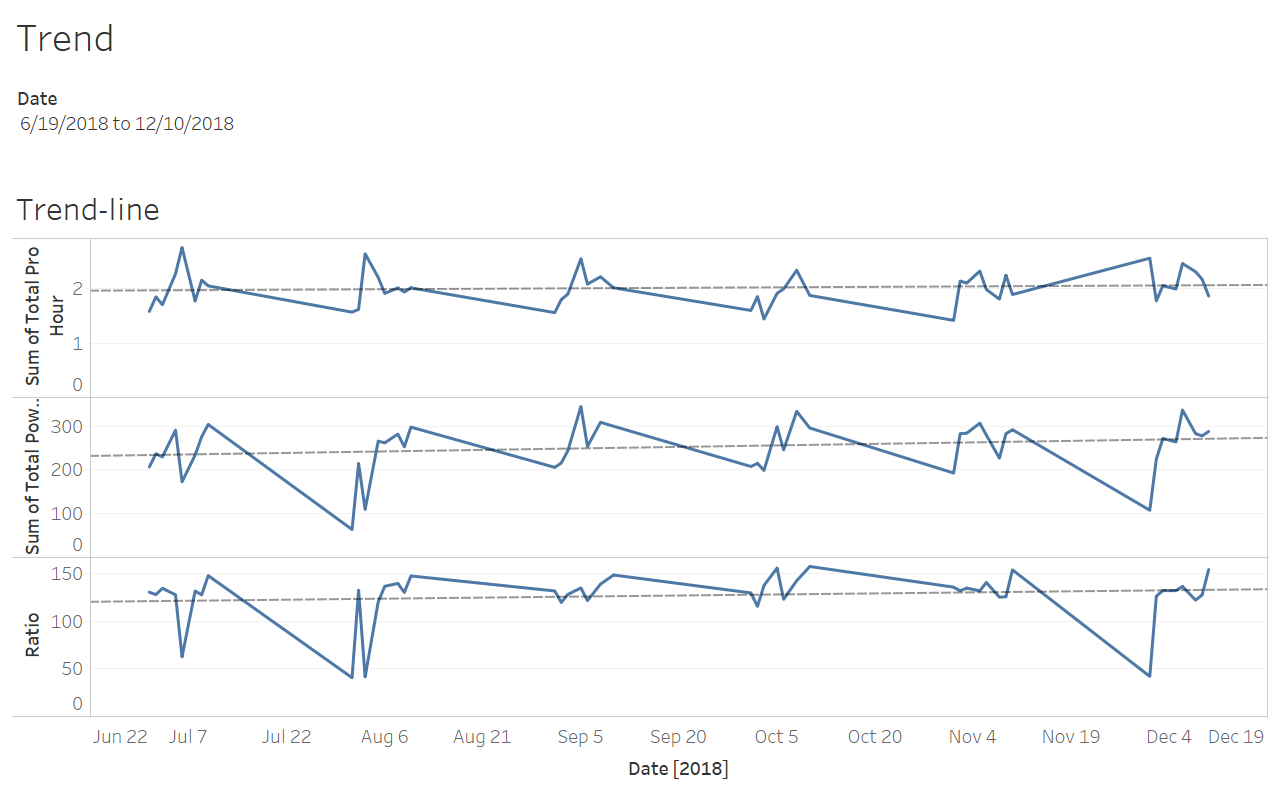
R
library(DBI)
library(RODBC)
library(RMySQL)
library(xts)
library(ggplot2)
library(hydroTSM) #call the hydrology package for time series analysis
#this code is used for energy audit of the plant based on production and power consumption
dataproduction = dbConnect(MySQL(), user='root', password='', dbname='exampledata', host='localhost')
#exampledata is the database stored in your MySQL server
dbListTables(dataproduction)
dbListFields(dataproduction, 'analysisdate')
rs = dbSendQuery(dataproduction, "select * from analysisdate")
rs=dbFetch(rs, n = -1)
data=c(rs[1],rs[4],rs[5],rs[6])
a=as.Date(data$date,"%Y-%m-%d")
production=data$total_pro_hour
power=data$total_power_hour
ratio=data$ratio
data=data.frame(a,production,power,ratio)
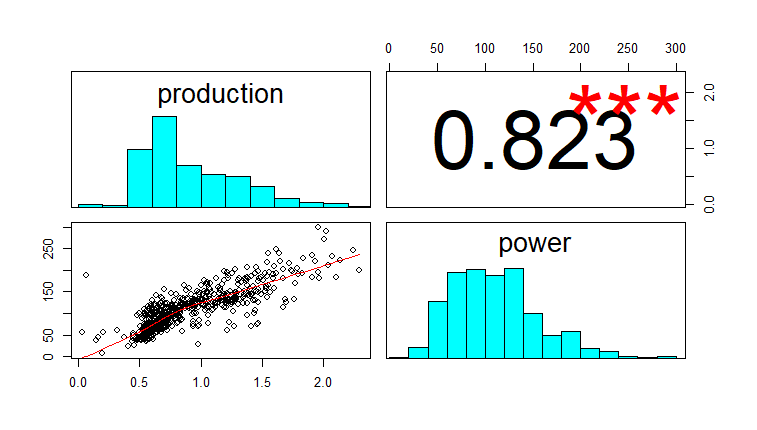
#Correlation analysis
hydropairs(data[,2:3])
#Plot production data
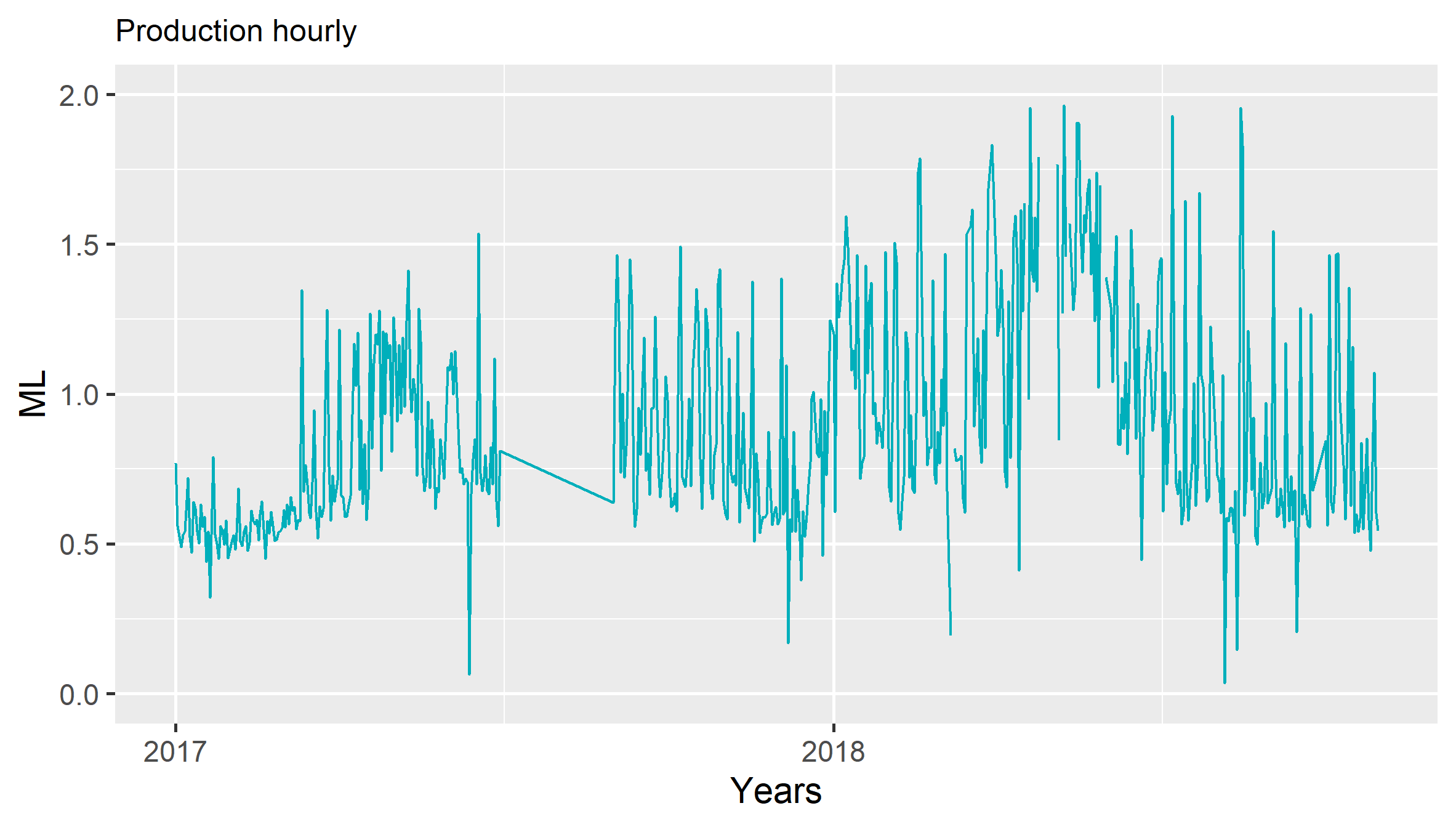
plot.new()
p=ggplot(data=data,aes(a, production))+ geom_line(color = "#00AFBB") + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 60,hjust=1))+theme_gray(base_size = 14)+ theme(plot.title = element_text(size=12))
p
min <- as.Date("2017-01-01")
max <- as.Date("2018-10-30")
#p + scale_x_date(limits = c(min, max))
pp=p+scale_x_date(date_labels = "%Y",date_breaks="year",limits = c(min, max))+labs(title = "Production hourly",x="Years",y="ML")+scale_y_continuous(limits=c(0,2))#+ stat_smooth(method="lm")
ggsave("ch05_fig_energy_production.png", plot = pp)
print(pp)
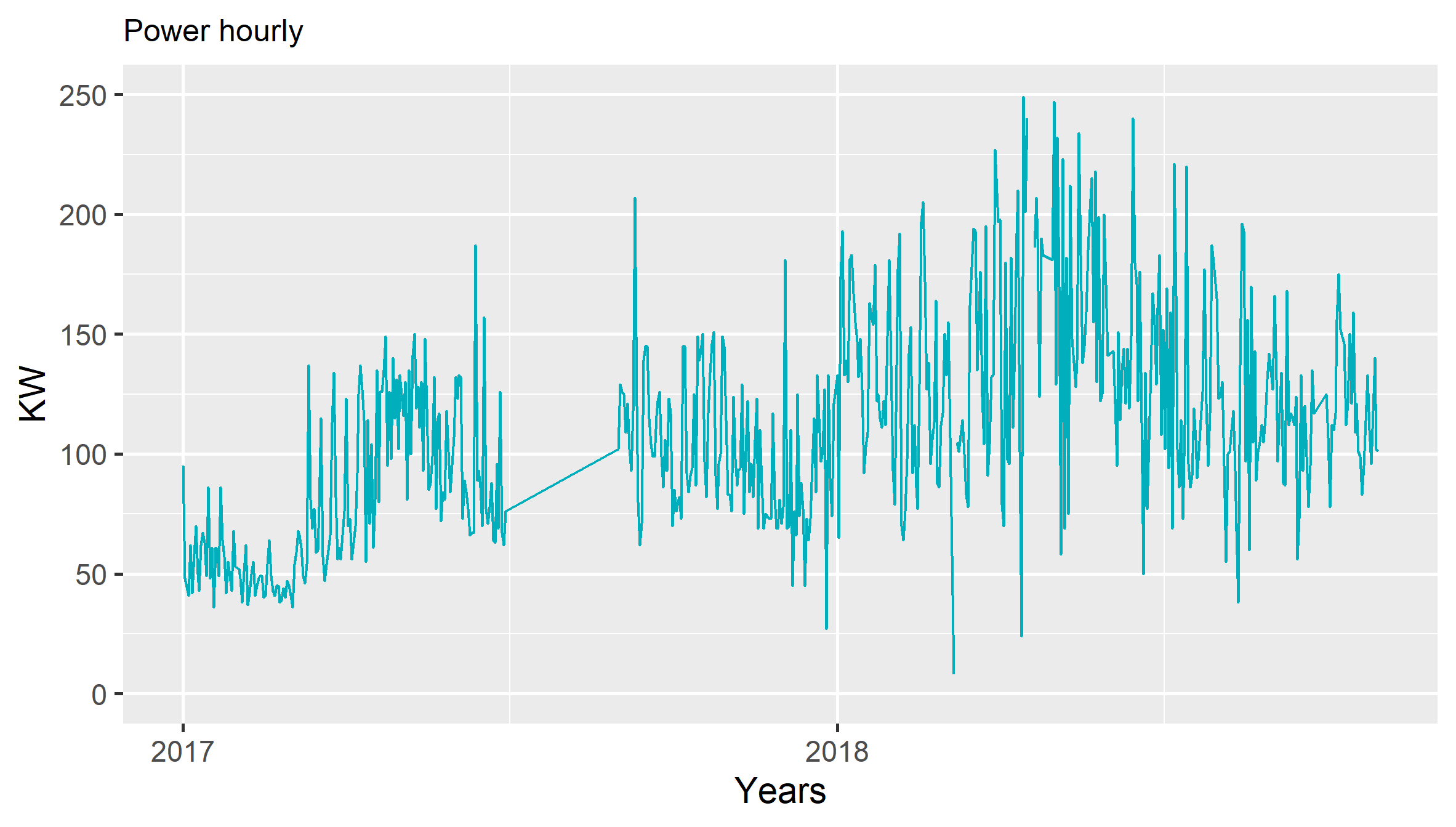
#Plot power consumption data
plot.new()
q=ggplot(data=data,aes(a, power))+ geom_line(color = "#00AFBB") + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 60,hjust=1))+theme_gray(base_size = 14)+ theme(plot.title = element_text(size=12))
#q
min <- as.Date("2017-01-01")
max <- as.Date("2018-10-30")
#p + scale_x_date(limits = c(min, max))
qq=q+scale_x_date(date_labels = "%Y",date_breaks="year",limits = c(min, max))+labs(title = "Power hourly",x="Years",y="KW")+scale_y_continuous(limits=c(0,250))#+ stat_smooth(method="lm")
ggsave("ch05_fig_energy_power.png", plot = qq)
print(qq)
#plot ratio
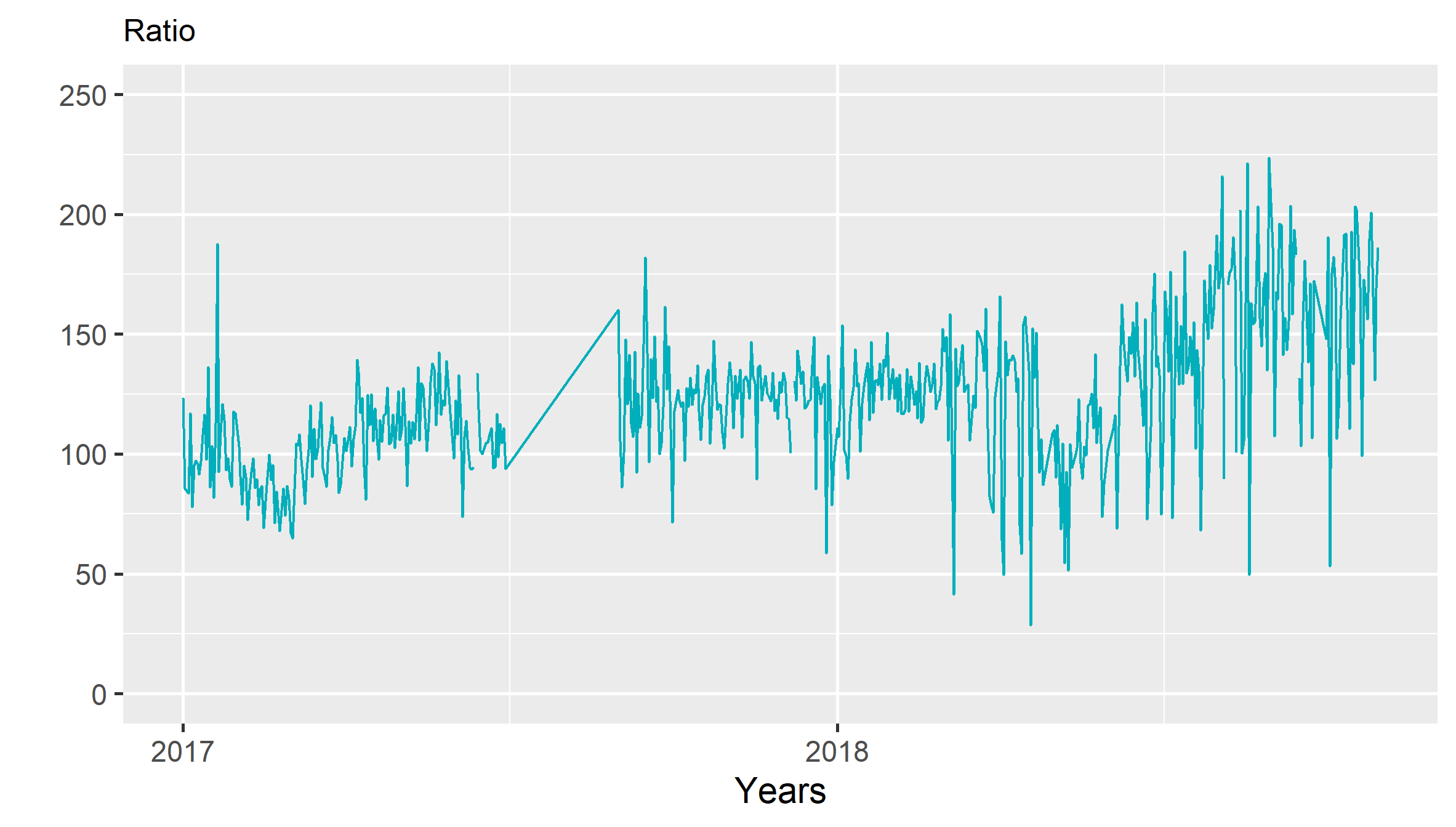
plot.new()
w=ggplot(data=data,aes(a, ratio))+ geom_line(color = "#00AFBB") + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 60,hjust=1))+theme_gray(base_size = 14)+ theme(plot.title = element_text(size=12))
#w
min <- as.Date("2017-01-01")
max <- as.Date("2018-10-30")
#p + scale_x_date(limits = c(min, max))
ww=w+scale_x_date(date_labels = "%Y",date_breaks="year",limits = c(min, max))+labs(title = "Ratio",x="Years",y="")+scale_y_continuous(limits=c(0,250))#+ stat_smooth(method="lm")
ggsave("ch05_fig_energy_ratio.png", plot = ww)
print(ww)
dbDisconnect(dataproduction)